Monitoring of cold energy leaks in Darwin, Australia
Realizing the importance of Urban Energy Waste and Urban Heat Island phenomena due to rapid urbanization not only in China but also in other parts of the world, scientists of HRSL, IRSA also conducted experiments in Darwin, Australia by using Modular Airborne Imaging Spectrometer (MAIS) which were reported in Australian newspaper in 1991. MAIS was the first real imaging spectrometer of China developed in early 1990s.
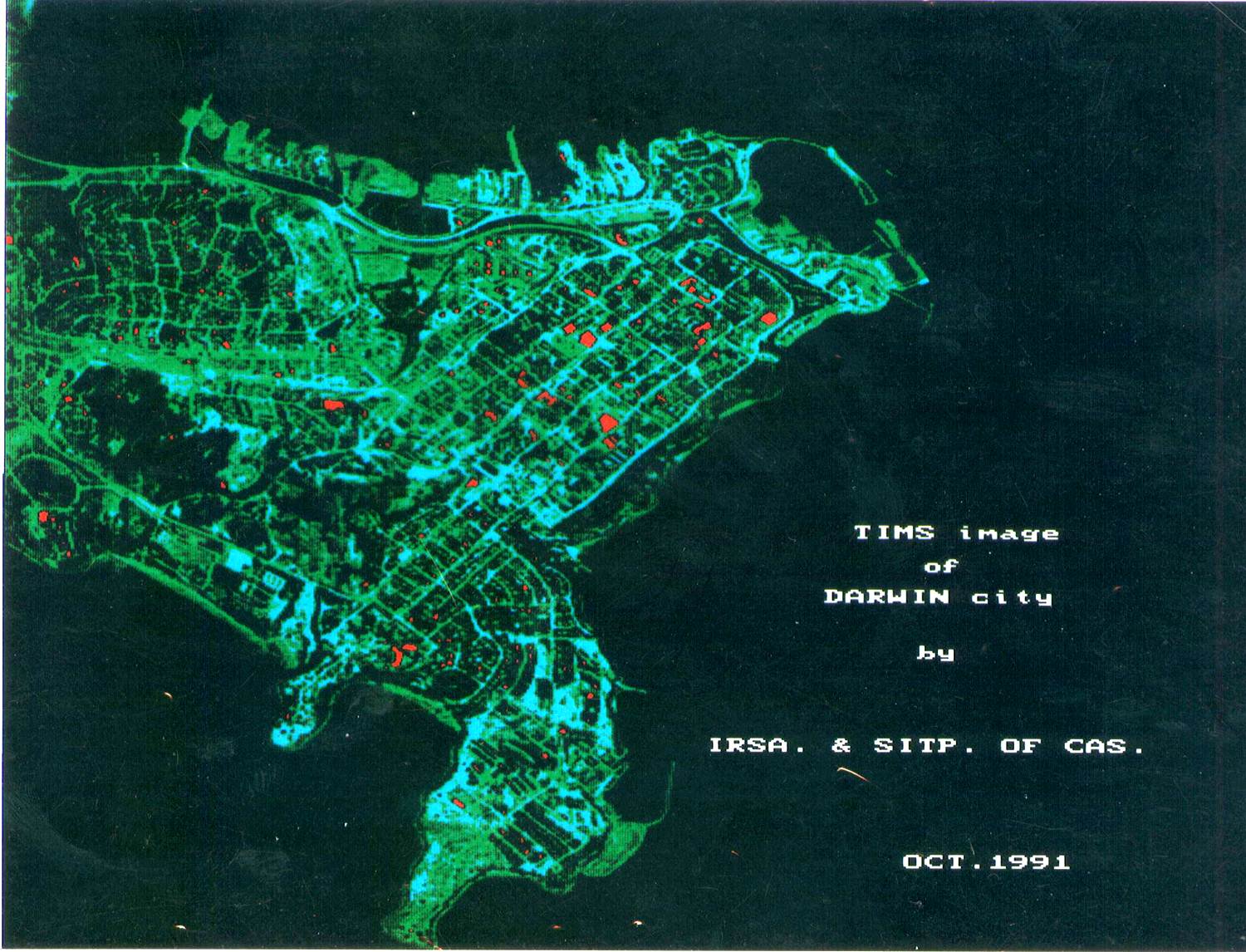
Figure: This historical image taken by using MAIS is showing the cool objects (red color) due to cold energy leaking from roofs of air-conditioned rooms.
The successful experiment was reported as “Hi-tech check shows energy waste in city” by AustraliaNews in 1991.These experiments highlighted the importance of imaging spectrometer for monitoring heat waste phenomena for the government agencies for proper management. These experiments were also conducted in different parts of China and provided valuable information to all stakeholders for future urban planning.
Reference:
Qingxi Tong, Yongqi Xue, Lifu Zhang. Progress of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Science and Technology in China overthePast Three Decades. IEEE JSTARS. 2014(7):70-91
